Error de formato de correo electrónico
emailCannotEmpty
emailDoesExist
pwdLetterLimtTip
inconsistentPwd
pwdLetterLimtTip
inconsistentPwd

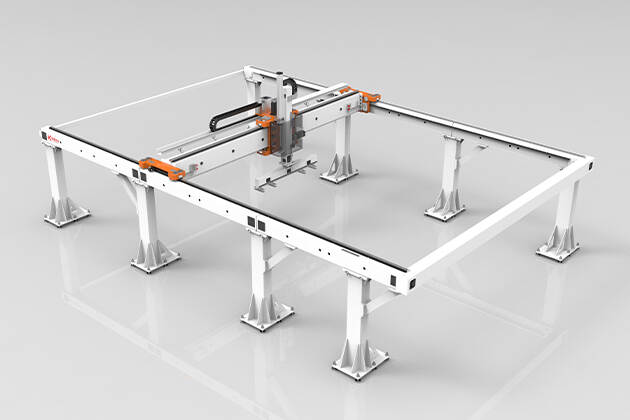
Differences Between Three-Axis and Two-Axis Gantry Robots
In the ever-evolving world of industrial automation, the choice between a Three-Axis Gantry Robot and a Two-Axis Gantry Robot can significantly impact the efficiency, versatility, and overall performance of your manufacturing processes. Both types of gantry robots offer unique advantages and are designed to meet specific needs, but understanding their differences is crucial for making an informed decision. Whether you are looking to enhance your production line, improve precision, or reduce labor costs, this guide will help you navigate the key distinctions and choose the right solution for your business.
Introduction to Gantry Robots
Gantry robots, also known as Cartesian robots, are widely used in various industries due to their precision, reliability, and flexibility. These robots operate on a Cartesian coordinate system, moving along linear axes to perform tasks such as pick-and-place, assembly, and material handling. The primary difference between Three-Axis Gantry Robots and Two-Axis Gantry Robots lies in their range of motion and the complexity of tasks they can handle.
Two-Axis Gantry Robots: Simplicity and Precision
Definition and Basic Functionality
A Two-Axis Gantry Robot, also known as a Cartesian robot or XY robot, operates along two perpendicular axes: the X-axis (horizontal) and the Y-axis (vertical or another horizontal direction). These robots are ideal for applications that require movement in a single plane. They are driven by servo motors or stepper motors and use common transmission methods such as ball screws, synchronous belts, and gear racks.
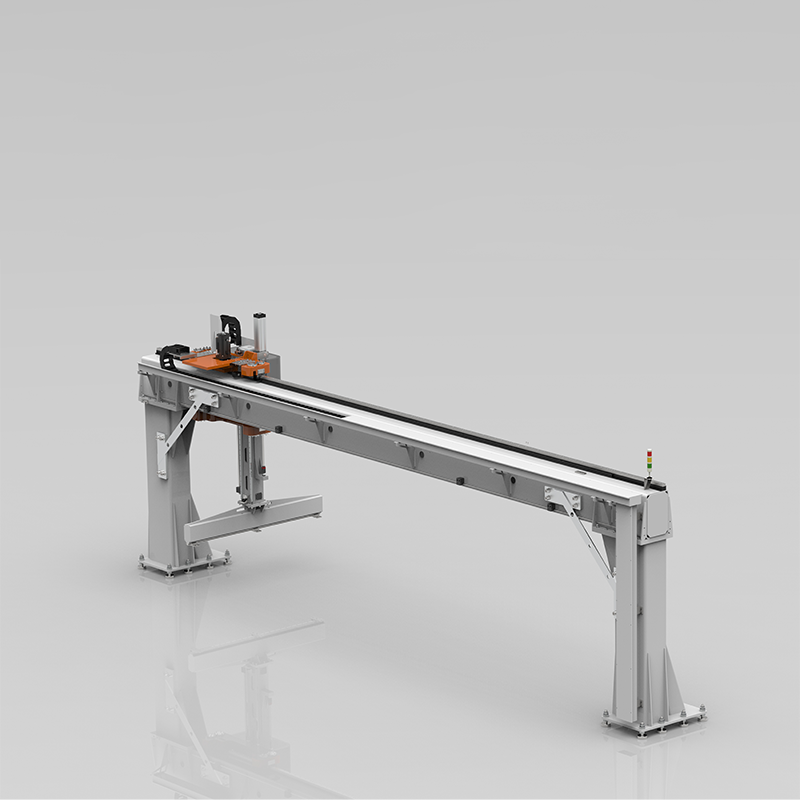

Key Features and Advantages
- Precision and Accuracy: Two-Axis Gantry Robots are highly precise and accurate, making them suitable for tasks that require exact positioning.
- Simplicity and Ease of Use: With fewer moving parts, these robots are easier to set up, program, and maintain.
- Cost-Effective Solution: They are generally more affordable than their three-axis counterparts, making them a cost-effective choice for many applications.
- Versatile Applications: Commonly used in PCB assembly, simple packaging, basic inspection, and other planar operations.
Applications and Use Cases
- PCB Assembly: Precise placement of components on printed circuit boards.
- Packaging: Simple and repetitive packaging tasks.
- Inspection: Quality control and inspection of flat surfaces.
- Material Handling: Moving items in a single plane, such as in conveyor systems.
Three-Axis Gantry Robots: Versatility and Complexity
Definition and Basic Functionality
A Three-Axis Gantry Robot adds a third axis, the Z-axis, which allows for vertical movement. This additional axis provides the robot with the ability to move in three dimensions, making it more versatile and capable of handling complex tasks. These robots are often used in environments where height adjustments and multi-level operations are required.
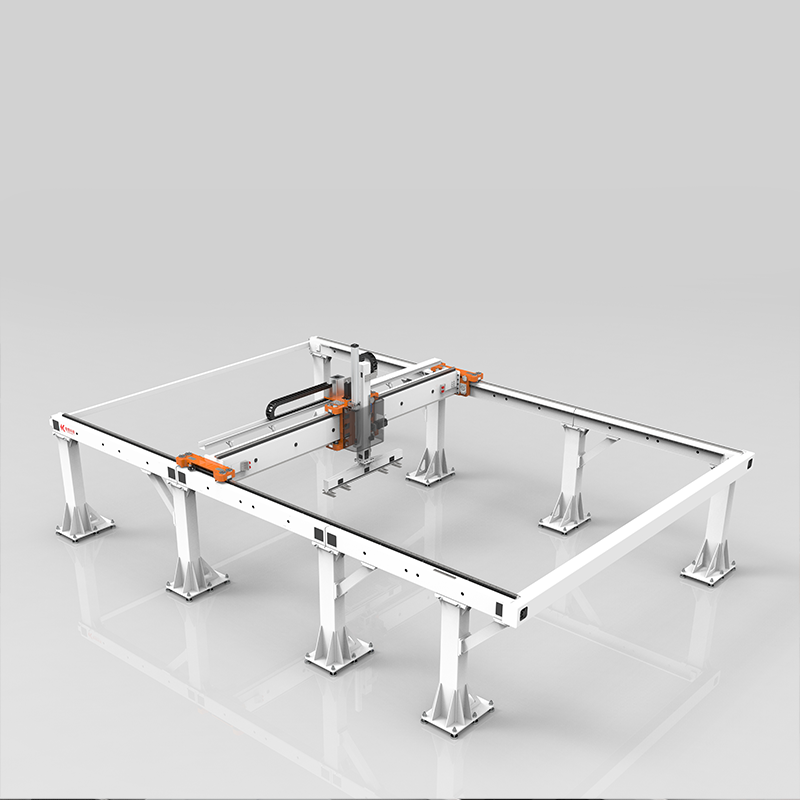
Key Features and Advantages
- Enhanced Flexibility: The addition of the Z-axis allows for movement in three dimensions, enabling the robot to reach different heights and positions.
- Complex Task Handling: Capable of performing more intricate tasks, such as 3D printing, complex assembly, and multi-level pick-and-place operations.
- High Speed and Efficiency: Designed for high-speed operations, making them ideal for fast-paced production lines.
- Customization and Integration: Can be customized and integrated with various CNC machines and other equipment to automate a wide range of processes.
Applications and Use Cases
- 3D Printing: Precise layer-by-layer deposition of materials.
- Complex Assembly: Assembly of components in multiple planes.
- Multi-Level Pick-and-Place: Handling items at different heights and positions.
- Advanced Inspection and Testing: Detailed inspection and testing of 3D objects.
- CNC Machine Tending: Automatic loading and unloading of workpieces in CNC machines.
Choosing the Right Gantry Robot for Your Needs
Factors to Consider
- Task Complexity: Determine the level of complexity required for your tasks. If your operations involve simple, planar movements, a Two-Axis Gantry Robot may suffice. For more complex, multi-dimensional tasks, a Three-Axis Gantry Robot is more appropriate.
- Budget: Consider your budget. Two-Axis Gantry Robots are generally more cost-effective, while Three-Axis Gantry Robots offer more features and capabilities.
- Space Constraints: Evaluate the available space in your facility. Three-Axis Gantry Robots may require more vertical clearance and space.
- Integration and Customization: Assess the need for customization and integration with existing equipment. Three-Axis Gantry Robots offer more flexibility in this regard.
Conclusion
Choosing between a Three-Axis Gantry Robot and a Two-Axis Gantry Robot depends on your specific requirements, including task complexity, budget, and space constraints. Both types of robots have their unique advantages and are designed to enhance the efficiency and precision of your manufacturing processes. By understanding the key differences and considering the factors outlined in this guide, you can make an informed decision that best meets your needs and drives your business forward.
If you have any questions or need further assistance in selecting the right gantry robot for your application, feel free to contact our team of experts. We are here to help you optimize your operations and achieve your goals.






